Lecithin and Psoriasis: Unraveling the Link


Intro
The intersection of lecithin and psoriasis presents an intriguing avenue for exploration in both nutritional science and dermatology. Lecithin, a phospholipid that occurs naturally in various biological systems, is gaining attention for its potential role in managing psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin disorder. This article will delve into the complex biochemical properties of lecithin, its sources, and its implications for psoriasis treatment.
Understanding how substances like lecithin interact with autoimmune conditions could unlock new pathways for therapeutic interventions. Research is beginning to highlight the need for deeper investigation into dietary factors that affect skin health.
One must approach the subject with a scientific lens, assessing existing literature and ongoing studies. As individuals increasingly seek natural remedies for chronic conditions, the relevance of lecithin in psoriasis management becomes more prominent.
Throughout this article, significant findings and methodologies will be addressed to provide a comprehensive overview of the topic. The ultimate aim is to equip readers—students, researchers, educators, and professionals—with embodied knowledge regarding the potential implications of lecithin on psoriasis and the avenues for future research.
Understanding Lecithin
Lecithin is a phospholipid that holds significant importance in cellular health and biological functions. Its role extends far beyond simple fat storage. This section takes a closer look at what lecithin is, how it functions in the body, and why its connection to psoriasis is worth examining. Understanding its properties is essential for appreciating its potential impact on skin health and disease management.
Definition and Composition
Lecithin is a complex mixture of phospholipids, primarily composed of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylserine. These components are vital for maintaining cellular integrity. Lecithin naturally occurs in various food sources, including egg yolks, soybeans, and sunflower seeds. Its emulsifying properties allow it to modulate fat digestion and absorption. This molecular structure forms the basis of many biological functions, influencing not just nutrition but also health at a cellular level.
Biochemical Role in the Body
The biochemical roles of lecithin in the human body are intertwined with several critical processes. Its contributions can be organized into three main areas:
Cell Membrane Structure
Lecithin plays a crucial role in forming and maintaining healthy cell membranes. The unique arrangement of phospholipids allows for flexibility and fluidity, enabling cells to function properly. Importantly, cell membranes also protect the cell's interior from external harm. This characteristic is critical in maintaining overall cell viability, making lecithin a critical component in cellular health.
Signal Transduction
In terms of signal transduction, lecithin is involved in transmitting messages across the cell membrane. This process is essential for cellular communication. By facilitating the binding of hormones and neurotransmitters to their receptors, lecithin aids in the regulation of various physiological reactions. Effective signal transduction assures that responses to environmental changes are timely and appropriate, supporting the notion of lecithin's potential therapeutic effects, especially in conditions like psoriasis.
Lipid Metabolism
Lecithin is also integral to lipid metabolism. It assists in the breakdown and distribution of fats through the body. By participating in the transport of lipids, lecithin ensures that essential fatty acids are available for biological processes. This role may contribute to skin health, given that skin barrier function is closely related to lipid profiles. A better understanding of lecithin's function in lipid metabolism could present new avenues for managing psoriasis, a condition often associated with systemic inflammatory responses.
"Lecithin is not just a nutrient; it is a vital component of cellular structures and functions across the human body."
The various aspects of lecithin support its contributions to skin health and potentially highlight an avenue for therapeutic intervention in conditions like psoriasis. With its ability to affect cellular integrity, communication, and nutrient metabolism, it becomes clear that a comprehensive understanding of lecithin is essential for exploring its implications in psoriasis treatment.
Overview of Psoriasis
Understanding psoriasis is critical when discussing its potential treatment options, including lecithin. Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that impacts the skin. Its influence extends beyond physical symptoms, affecting emotional and mental well-being. Knowing the types and mechanisms of psoriasis provides insight into how lecithin might play a role in its management. This section will clarify psoriasis's fundamental aspects, which are vital for comprehending potential therapeutic interventions.
Definition and Types
Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most common form of psoriasis, affecting nearly 80-90% of those diagnosed. This type is characterized by raised, red patches covered with thick, silvery scales. The visibility of these patches can lead to psychological discomfort for patients. Effectively, plaque psoriasis serves as a focal point for understanding the condition as a whole. Its prominence in discussions about psoriasis makes it a critical type to examine, especially regarding management strategies.
A distinctive feature of plaque psoriasis is the location. It typically appears on the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp, leading to significant discomfort in these areas. Understanding this aspect is beneficial as it informs both the clinical approach and treatment guidelines.
Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis often appears suddenly, typically following a streptococcal infection. This type is less common, affecting a smaller group of individuals. The characteristic features include small, droplet-shaped lesions scattered across the trunk and limbs. Recognizing guttate psoriasis is essential for identifying treatment pathways since it can manifest differently from plaque psoriasis.
One unique aspect is its potential to resolve spontaneously. Many cases of guttate psoriasis have a temporary nature, presenting notable advantages and disadvantages concerning treatment. While some patients may require minimal intervention, others may see relapses that necessitate comprehensive management approaches.
Inverse Psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis occurs in skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, or under the breasts. This characteristic location makes it distinct from other forms. Patients with inverse psoriasis might face significant irritation due to the friction in these areas. Understanding inverse psoriasis deepens the knowledge of various patient experiences and treatment challenges.
Its unique feature lies in the smooth and red lesions that form, often prone to irritation. This adds a layer of complexity to treatment and management strategies, highlighting the need for tailored interventions.
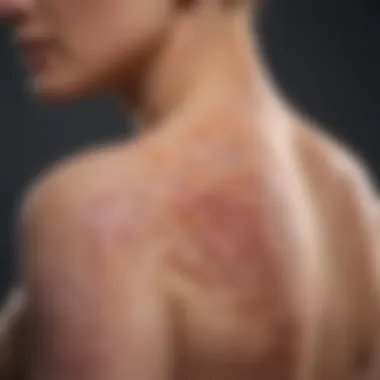

Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of psoriasis is complex, primarily driven by the immune system. Understanding this dimension is vital for appreciating how lecithin and other dietary interventions may influence treatment.
Immune System Involvement
Psoriasis is fundamentally an immune-mediated condition. The immune system's overreaction leads to inflammation and increased skin cell production. This role of the immune system is critical to understanding the disease. Targeting immune responses is a significant focus of many psoriasis treatments, and understanding these mechanisms is crucial when considering lecithin's potential impact.
One key feature is the involvement of T-cells, which play a substantial role in the inflammatory response. Their activation leads to the symptoms associated with psoriasis. This connection underscores the importance of immune system modulation in treatment strategies.
Genetic Factors
Genetics undoubtedly contributes to psoriasis. Certain genetic markers have been identified that increase susceptibility to the disease. Knowledge of genetic factors allows researchers to explore personalized treatment plans that may incorporate lecithin as part of a broader dietary approach.
The unique feature here is that not all individuals will express psoriasis symptoms, even if they possess the genetic predisposition. This variability presents both challenges and opportunities in treatment, making it a significant consideration in this article.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors also play a key role in triggering psoriasis flares. These triggers vary widely, including stress, skin injury, and certain infections. Understanding these aspects broadens the perspective on psoriasis treatment options.
One important characteristic is the interaction between genetic predisposition and environmental factors. Notably, general recommendations for managing triggers can help reduce flare-ups, offering practical approaches alongside pharmacological interventions. Understanding and addressing these triggers can enhance treatment efficacy.
Lecithin's Potential Impact on Skin Health
Lecithin is increasingly recognized for its potential benefits in skin health, particularly regarding conditions like psoriasis. Psoriasis, an inflammatory skin disorder, often presents unique challenges that may be addressed by dietary and supplemental sources of lecithin. Understanding the implications of lecithin on skin health is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. This section will explore the mechanisms through which lecithin may influence skin health, alongside the research supporting these claims.
Mechanisms of Action
Hydration and Barrier Function
Hydration is a critical aspect of skin health. Lecithin plays a significant role in maintaining skin hydration and integrity. It serves as a natural emollient that helps to keep the skin moist and protects against environmental aggressors. One of its main characteristics is its phospholipid content, which facilitates the formation of a lipid barrier on the skin's surface. This barrier reduces transepidermal water loss, which is beneficial for conditions like psoriasis, where the skin often becomes dry and flaky.
The unique feature of hydration through lecithin is its compatibility with skin lipids, making it an effective moisturizer and barrier enhancer. This characteristic is particularly advantageous, as it directly addresses one of the fundamental issues in psoriasis management—dryness and barrier dysfunction.
Inflammation Modulation
Lecithin also appears to play a role in modulating inflammation, which is central to the pathophysiology of psoriasis. It may contribute to the regulation of inflammatory pathways and cytokine signaling, helping to reduce the inflammatory response in the skin. This aspect is crucial because excessive inflammation exacerbates psoriatic lesions.
The key characteristic here is lecithin’s ability to interact with immune cells and modulate their activity. This modulating effect may provide a beneficial approach to minimizing flare-ups associated with psoriasis. However, the challenge lies in determining the right dosage and long-term effects on inflammation in individuals.
Antioxidant Properties
The antioxidant properties of lecithin are another important aspect to consider. Oxidative stress is known to worsen psoriasis symptoms, and lecithin’s antioxidant compounds may help counteract this effect. By scavenging free radicals, lecithin contributes to reducing oxidative damage in skin cells.
This characteristic of lecithin is beneficial in promoting skin health, especially in inflammatory conditions. The unique feature of its antioxidant activity can provide skin with additional protection against environmental and metabolic stressors. Despite this, how effective lecithin is as an antioxidant in practical terms compared to other antioxidants remains to be fully clarified.
Research Evidence
Clinical Studies
Clinical studies focusing on lecithin and skin health are relatively scarce but suggest promising results. Some research indicates that including lecithin in dietary intake may help improve certain markers of skin barrier function. The specific characteristics of these studies often include small sample sizes and varying methodologies, which complicates the establishment of clear conclusions.
The potential advantage of clinical studies lies in their ability to provide direct evidence regarding the effectiveness of lecithin supplementation. However, the diversity in study outcomes signifies the necessity for more rigorous research in this field.
Observational Research
Observational research on lecithin and its effects on skin health indicates that people who consume diets rich in lecithin may have improved skin conditions. This type of research allows for the observation of larger populations over longer durations compared to controlled trials. Such studies underscore the importance of eating habits over time, suggesting relationships between lecithin intake and skin health improvements.
Observational studies provide valuable insights but may suffer from bias and confounding variables. Understanding these limitations is critical when interpreting results from this type of research.
Case Reports
Case reports provide anecdotal evidence regarding the impact of lecithin on skin health, especially in individual cases of psoriasis. While they often highlight notable improvements in patients who incorporate lecithin into their regimen, these reports lack systematic control and generalizability.


The unique feature of case reports is their ability to illustrate real-world applications and outcomes. However, they should be interpreted cautiously, as evidence from case studies alone is insufficient to draw broad conclusions about lecithin's efficacy in treating psoriasis.
"The focus on the relationship between lecithin and skin health illuminates potential pathways for new therapeutic strategies in psoriasis management."
Dietary Sources of Lecithin
The role of lecithin in diet cannot be overstated, especially when considering its potential connection to skin health and psoriasis management. Lecithin is a phospholipid that is naturally present in various food items. By understanding its dietary sources, individuals may enhance their consumption of this important nutrient, potentially benefiting their overall health and skin condition.
Natural Food Sources
Egg Yolks
Egg yolks are one of the richest natural sources of lecithin. They contain high levels of phospholipids, contributing positively to cell membrane structure and function. Egg yolks are often viewed as a beneficial choice due to their nutrient density, providing not only lecithin but also vitamins A, D, E, and B12. One distinct advantage of egg yolks is their high bioavailability, which means the body can efficiently utilize the nutrients contained within them. However, for some people, especially those concerned about cholesterol levels, the consumption of egg yolks may raise concerns. Thus, moderation is key.
Soybeans
Soybeans are another significant source of lecithin, often found in various forms, including soy milk and tofu. The lecithin extracted from soybeans is commonly used in food production as an emulsifier. Soybeans are favored for their plant-based protein content and are often a staple in vegetarian and vegan diets. A key characteristic of soybean lecithin is its relatively low cost and wide availability, making it a popular choice among consumers. However, some individuals may have soy allergies, limiting their ability to include this food source in their diet.
Sunflower Seeds
Sunflower seeds are an excellent plant-based source of lecithin as well. These seeds not only provide lecithin but also offer a range of nutrients like vitamin E, magnesium, and selenium. A significant advantage of sunflower seeds is that they are generally safe for individuals with soy allergies. They can be eaten as a snack, added to salads, or used in various recipes. One notable feature is their versatility, allowing them to be more easily incorporated into diets compared to other sources. However, they are energy-dense, and overconsumption can lead to increased caloric intake, which is a consideration for those monitoring their weight.
Lecithin Supplements
Types of Lecithin Supplements
Lecithin supplements are available in various forms, including liquid, granules, and softgels. These supplements can provide a concentrated source of lecithin, which may be more convenient than food sources for some individuals. Different types include soy lecithin and sunflower lecithin. Sunflower lecithin is often seen as a preferred option for those avoiding soy. The distinct characteristic of these supplements is their convenience and potentially higher concentrations of lecithin. However, reliance on supplements may lead to missed opportunities to gain beneficial nutrients from whole food sources.
Dosage Considerations
The effectiveness of lecithin supplements can be influenced by the dosage taken. Typical recommended dosages range from 1 to 3 grams per day. Adjusting the dose may depend on individual health needs and conditions. A key characteristic is the possibility of gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea or nausea, particularly at higher doses. Thus, individuals should consider their tolerance levels and consult with healthcare providers before starting supplementation.
Safety and Side Effects
While lecithin is generally considered safe for most people, some may experience adverse effects. Potential side effects include gastrointestinal issues and allergic reactions, particularly in those with soy allergies. A critical aspect to consider is that individuals should monitor their body’s response when introducing lecithin into their diet, whether through food or supplements. It's essential to inform oneself about possible contraindications and interactions with medications. This careful approach ensures that the benefits of lecithin are enjoyed while minimizing risks.
Evaluating the Efficacy of Lecithin in Psoriasis Treatment
The topic of evaluating the efficacy of lecithin in psoriasis treatment is essential because of the potential therapeutic benefits associated with lecithin's biochemical properties. Given psoriasis’ chronic nature, finding effective treatment methods is paramount for the wellbeing of patients. Lecithin may offer a novel approach, but understanding its overall impact requires thorough investigation.
Exploring ∗clinical implications∗, including how lecithin could serve as a complementary therapy alongside conventional treatments, can provide valuable insights. It offers possible enhancements in skin health and symptom management for individuals suffering from psoriasis. Identifying the specific mechanisms through which lecithin exerts its effects will help determine its place in treatment protocols.
The evaluation of current guidelines and recommendations is necessary to gauge the acceptance of lecithin in the therapeutic landscape. It is crucial to align scientific findings with the advice provided to healthcare professionals and patients, ensuring that their decisions are informed by the latest research.
Furthermore, this section synthesizes existing knowledge and identifies gaps in research, which may direct future studies. Advances in understanding how lecithin interacts with psoriasis can contribute to evidence-based practices and optimization of treatment strategies.
Clinical Implications
The clinical implications of using lecithin in the treatment of psoriasis are worth examining. Lecithin's roles in maintaining cell membrane integrity and modulating inflammation suggest it could be beneficial. Psoriasis involved an inflammatory response, and lecithin might contribute to the modulation of this process. Here are some key points:
- Barrier Function: Improved barrier function could lead to better skin hydration, potentially reducing psoriasis flares.
- Inflammation Control: Lecithin could aid in managing the inflammatory response that characterizes psoriasis, possibly reducing the severity and frequency of outbreaks.
- Synergistic Therapy: When combined with existing therapies, lecithin may enhance overall treatment effectiveness without the need for increased medication dosages.
Overall, continued exploration into the clinical implications of lecithin brings promise, but it should be approached with careful consideration of its effects and limitations.
Current Guidelines and Recommendations
Current guidelines and recommendations regarding lecithin in psoriasis treatment are still developing. Healthcare providers often depend on established treatments, such as topical therapies and systemic medications. Lecithin is not yet broadly recognized within most guidelines primarily due to a lack of extensive research.
It is important to consider the following points:
- Literature Review: Recent studies suggest potential benefits but more comprehensive data is needed to integrate lecithin into formal treatment guidelines.
- Consultation with Professionals: Patients interested in using lecithin should consult with healthcare professionals to address concerns and judge personal suitability.
- Monitoring Outcomes: If lecithin is adopted, it's vital to monitor patient outcomes systematically to evaluate its effectiveness and adjust recommendations accordingly.


Future Research Directions
Understanding the future research directions regarding lecithin and psoriasis is vital for several reasons. First, as the knowledge base grows about both lecithin's biochemical properties and the complexities of psoriasis, there are emerging avenues for exploration that could lead to better treatment protocols. Psoriasis remains a challenging condition for many patients, and identifying effective treatments is of paramount importance.
In addressing this, the focus on specific research areas can contribute not only to clinical practices but also to the overall understanding of lecithin's role. Identifying dosage, long-term effects, and mechanistic insights offers a structured approach to unraveling the relationship between lecithin and psoriasis management. Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaborations may bridge gaps that exist in current research, collectively enhancing treatment outcomes.
Areas for Further Investigation
Dosage and Formulation Studies
Investigating appropriate dosage and formulation of lecithin may lead to more effective treatment strategies. Different forms of lecithin exist, like granules, capsules, and liquid preparations, and each may have varying bioavailability.
Understanding which formulation is optimal for psoriasis could enhance lecithin's therapeutic effects. However, dosing variability poses challenges; determining the right amount is crucial to maximizing benefits without complications. A well-established dosage can provide clear guidelines for healthcare providers and patients alike.
Long-term Effects
Studying the long-term effects of lecithin is particularly crucial for developing sustainable psoriasis management strategies. Chronic conditions require treatments that are safe over extended periods.
By examining the sustained use of lecithin, researchers can assess its safety profile and any potential side effects. This information is important for patients who may consider long-term lecithin supplementation. Additionally, understanding how prolonged exposure to lecithin influences psoriasis symptoms can contribute to effective treatment regimens.
Mechanistic Insights
Gaining mechanistic insights into how lecithin interacts with biological systems is essential. Analyzing these interactions can uncover how lecithin contributes to skin health, particularly in the context of psoriasis.
A better understanding of these mechanisms could inform how to integrate lecithin into existing psoriasis treatments. Studies focused on mechanisms also allow researchers to pinpoint whether lecithin directly influences inflammation or appears to modulate other pathways. This focus can provide a deeper understanding of the therapeutic potential of lecithin in dermatological contexts.
Interdisciplinary Approaches
Combining Lecithin with Other Treatments
Investigating the synergy between lecithin and other treatment strategies can pave the way for innovative approaches to manage psoriasis. Combining lecithin with existing medications might enhance their effectiveness or offset side effects. This approach also opens the door for personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual patient's needs.
Moreover, exploring how lecithin can complement therapies examines not just its standalone effects but also its potential collaborative benefits. Such interdisciplinary approaches could deliver more comprehensive care models for psoriasis patients.
Nutritional Interventions
Exploring nutritional interventions, including lecithin intake through diet, is another significant area for research. Studies that focus on food sources rich in lecithin, such as eggs and soy, can offer evidence about dietary impacts on psoriasis.
Nutrition plays a crucial role in overall health, and understanding how lecithin as part of diet can influence psoriasis outcomes could lead to recommendations that help patients manage their condition holistically. This research could shed light on dietary guidelines that incorporate lecithin while addressing the specific needs of psoriasis sufferers.
Patient-Centric Studies
Emphasizing patient-centric studies is vital for understanding real-world applications of lecithin in psoriasis treatment. These studies focus on patient experiences, preferences, and outcomes, thus highlighting practical considerations.
Conducting these studies can provide insights that clinical trials may overlook, particularly regarding quality of life improvements and patient satisfaction. This perspective ensures that research aligns well with patient needs, ultimately bridging the gap between theory and practice in psoriasis management.
Culmination
The conclusion serves as a vital part of any scholarly article. In this discussion of lecithin and psoriasis, it synthesizes all previous insights into a coherent narrative that highlights the significance of the subject. It is not merely a summary but an opportunity to reflect on the findings related to lecithin's biochemical properties and its possible implications for psoriasis management.
The importance of lecithin in the context of psoriasis cannot be overstated. Many studies hint at its potential effects on skin health, specifically through mechanisms such as hydration, barrier function, and modulation of inflammation. As psoriasis is an autoimmune condition characterized by elevated inflammation, understanding the connections with lecithin could open new avenues for treatment.
Moreover, the research indicates that dietary sources of lecithin, along with supplementation, might have notable benefits. This makes it a relevant topic for those affected by psoriasis or those researching its underlying mechanisms and management strategies.
Ultimately, the conclusion illuminates the need for further exploration to establish clear guidelines on lecithin's efficacy in psoriasis. It calls for additional interdisciplinary studies that blend nutritional interventions, dermatological insights, and patient-centered approaches. Such work is imperative to offer a more holistic perspective on treating psoriasis effectively.
Summary of Findings
In the previous sections, we examined the multifaceted connections between lecithin and psoriasis. Here are the key findings:
- Lecithin Biochemistry: Lecithin is a vital phospholipid contributing significantly to cell membrane structure and function in the body.
- Skin Health: Lecithin possesses hydrating, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties that can affect skin integrity and overall health.
- Research Evidence: Current literature presents mixed evidence about the role of lecithin in managing psoriasis. Some clinical studies and case reports suggest positive outcomes.
- Dietary Sources: Natural food sources of lecithin, such as egg yolks and soybeans, are accessible, and supplementation can be considered based on individual needs.
- Clinical Implications: Understanding the impact of lecithin offers valuable insights into possible supplemental therapies alongside traditional psoriasis treatments.
Final Thoughts on Lecithin and Psoriasis
In closing, the exploration of lecithin's role in psoriasis management opens intriguing possibilities for both patients and researchers. While substantive findings have emerged, it is evident that further investigation is warranted to draw definitive conclusions.
The interplay of nutrition and autoimmune conditions like psoriasis is increasingly recognized in modern medicine. Lecithin's potential as a complementary therapeutic target invites a reevaluation of dietary practices and treatment regimens.
As this field continues to evolve, the implications of lecithin become clearer. Ongoing research will likely provide more substantial insights, which could ultimately help in devising effective management strategies for psoriasis. The road ahead demands diligence and collaboration among disciplines to create a comprehensive understanding aimed at improving patient outcomes.



