Mastering Pressure Reducer Valve Adjustments

Intro
Adjusting a pressure reducer valve is a crucial task for maintaining optimal pressure in various systems. This process is relevant both for novices and experienced technicians. A pressure reducer valve serves to lower the pressure from a supply point to a desired level suitable for downstream operations. Understanding how to adjust these valves can enhance safety, improve efficiency, and prolong the lifespan of connected equipment.
This guide will delve into the key findings about pressure reducer valves, methodologies for adjustment, safety considerations, and potential troubleshooting techniques. By following the outlined steps, you can ensure proper functionality of your valve, effectively managing the pressure within the system.
Preface to Pressure Reducer Valves
Pressure reducer valves play a pivotal role in managing fluid systems across various applications. Understanding their functions and operational mechanisms is essential for effective use. These valves ensure that the pressure of a fluid supply is lowered to a safe and usable level. Without proper management of pressure, systems can become inefficient, lead to equipment damage, or create unsafe working conditions.
Definition and Purpose
A pressure reducer valve is a device that reduces and stabilizes the pressure of fluid flowing through a system. Its primary function is to maintain a set outlet pressure despite variations in input pressure. This is critical for ensuring the efficient operation of equipment and the safety of processes. In essence, the valve acts as a regulator, allowing systems to function within designed pressure limits, thus preventing unnecessary strain and potential failure of connected devices.
Applications of Pressure Reducer Valves
These valves find use in a wide range of industries, including:
- Water Supply Systems: They ensure consistent water pressure for municipal and residential systems.
- Gas Distribution: Used to regulate pressure in pipelines to ensure safe delivery.
- HVAC Systems: These valves help maintain pressure for various heating and cooling applications.
- Industrial Machinery: Essential for optimizing pressure in hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
In summary, pressure reducer valves are not just components of a system; they are critical in ensuring efficiency and safety across multiple applications. Recognizing their importance forms the foundation for understanding the adjustment process, which will be explored in the following sections.
Understanding Pressure Reduction Mechanisms
Understanding pressure reduction mechanisms is crucial for anyone dealing with systems that require controlled pressure levels. This knowledge ensures that users can effectively manage the operational efficiency and safety of hydraulic or pneumatic systems. Knowing how pressure reduction works allows individuals to make informed decisions regarding adjustments and maintenance.
Mechanics of Pressure Reduction
The mechanics of pressure reduction primarily involve the manipulation of fluid dynamics. Pressure reducer valves alter the flow pressure by regulating the amount of fluid that can pass through the valve at any given time. Essentially, when high pressure enters the valve chamber, the valve modulates this pressure to a predefined lower level.
Components such as springs, diaphragms, and seals work together to create a consistent output pressure. Understanding how these components interact provides insight into improving system efficiency and minimizing potential hazards. A failure to understand this mechanism can lead to fluctuations in pressure, which may result in equipment damage or unsafe working conditions.
Key aspects include:
- Pressure Control: Maintaining the desired pressure levels for optimal performance.
- Flow Regulation: Controlling the flow rate, which affects system efficiency.
- Safety Mechanisms: Preventing over-pressurization that could lead to catastrophic failure.
Types of Pressure Reducer Valves
Pressure reducer valves come in various types, each suited for different applications and pressure requirements. Here are some commonly used types:
- Spring-Loaded Valves: These utilize a spring mechanism to maintain a fixed pressure. They are straightforward and widely used in many applications.
- Pneumatic Valves: Used primarily in air systems, these valves adjust air pressure, allowing for precise control of pneumatic tools and processes.
- Electronic Pressure Regulators: These valves use electronic sensors for real-time pressure monitoring and adjustment. They are suitable for advanced applications requiring high precision.
- Pilot-Operated Valves: These take input from a pilot signal to adjust the primary pressure, offering enhanced stability under varying flow conditions.
Understanding the types of pressure reducer valves enables users to choose the right one for their specific needs. Each type has its advantages and suitability depending on the complexity and demands of the system in which it is used.
"The choice of valve directly influences system performance and reliability."
While selecting a valve, one must consider factors such as operational range, the type of fluid, and environmental conditions. This ensures that the chosen valve accommodates the specific application effectively.


Pre-Adjustment Considerations
Before adjusting a pressure reducer valve, it is crucial to take several key factors into account. These pre-adjustment considerations form the foundation of an effective adjustment process. Without a proper assessment and understanding of current conditions, any adjustments made may lead to ineffective pressure control or, worse, cause system malfunctions. Therefore, approaching the adjustment task with diligence is essential.
Assessing Current Pressure Levels
Understanding the current pressure levels in your system is the first step. You need to measure pressure accurately using a gauge. This gauge will provide insights into both upstream (input) and downstream (output) pressures. Take readings when the system is both at rest and in operation. Fluctuations in pressure may indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed before making any adjustments.
Identifying Pressure Requirements
Each application has its unique pressure requirements. It is important to outline what pressure levels your system should maintain. Factors such as equipment specifications, operational needs, and safety parameters should guide this assessment. Gather information on the desired operating pressure for your specific applications to ensure that you balance efficiency with safety.
Reviewing Manufacturer Specifications
Finally, reviewing the manufacturer's specifications ensures that you have all necessary details at your fingertips. The documentation provided typically includes the factory settings for pressure, as well as any limitations of the equipment in terms of pressure range. By cross-referencing your current system performance against these standards, you can identify the adjustments needed more effectively.
"Properly understanding these pre-adjustment factors can save time and resources, leading to more efficient pressure management in various applications."
In summary, these pre-adjustment considerations are critical to a successful adjustment process. They set the stage for an informed, precise, and safe adjustment experience.
Step-by-Step Guide to Adjusting the Valve
Adjusting a pressure reducer valve requires a systematic approach. The importance of this step-by-step guide cannot be understated. Each action taken influences the overall system performance, ensuring optimal pressure management. Accurate settings enhance equipment longevity and operational efficiency. Individuals who understand these steps improve their capability to mitigate potential risks associated with incorrect pressure levels.
Gathering Required Tools
Before embarking on the adjustment process, it is important to gather the necessary tools. Having everything at hand reduces interruptions during the procedure. Key tools typically include a pressure gauge, adjustable wrenches, and screwdrivers. However, depending on specific valve types, additional tools might be necessary. Always review the valve's user manual to confirm the required tools for that model.
Shutting Down the System Safely
Safety should be the highest priority during any maintenance task. Before adjustments can begin, you must safely shut down the system connected to the pressure reducer valve. This often involves:
- Disconnecting power sources.
- Releasing existing pressure in the system.
- Allowing the system components to cool, if necessary.
Ensuring these steps are followed can prevent accidents and equipment damage during the adjustment process.
Locating the Adjustment Mechanism
After shutting down the system, locate the adjustment mechanism on the pressure reducer valve. This may vary by design but typically exists as a screw or knob on the top or side of the valve. Visually inspect the valve and consult the manual to understand the exact location. Understanding where to make adjustments is critical for successful calibration.
Making Initial Adjustments
With the adjustment mechanism identified, it's time to make initial changes. Start by loosening the adjustment screw or knob slightly. Gradually turn it to raise or lower the pressure as required by your system’s specifications.
It's recommended to make these adjustments in small increments. This allows users to monitor the pressure changes effectively. Ensuring precision in this phase will establish a strong foundation for effective pressure control.
Testing Pressure Levels Post-Adjustment
Finally, it’s crucial to test the pressure levels after adjustments. Restart the system and observe the pressure gauge closely. Compare the readings to the required specifications obtained earlier. It may be necessary to repeat the adjustment process if the readings do not align with desired outcomes.Often, it takes a few tries to reach the optimal pressure.
Proper testing prevents future complications and enhances system performance.
Repeat the testing process until stable pressure readings are achieved. This final step ensures the pressure reducer valve functions as intended.
Post-Adjustment Considerations
After adjusting a pressure reducer valve, it is essential to monitor and evaluate the system's performance closely. Post-adjustment considerations help ensure that the modifications made lead to desired outcomes without introducing new issues. This section will discuss the importance of continuous observation and documentation of changes following the adjustment process. These practices enhance reliability and efficiency in the system’s operation.
Monitoring System Performance
Monitoring the system performance is a critical component after the adjustment of a pressure reducer valve. Once adjustments have been made, it is vital to assess the system’s response to the new pressure settings. A systematic approach to monitoring can include several key elements:
- Pressure Readings: Frequently check the pressure levels using a reliable manometer to confirm the adjustments hold. Compare these readings to the specifications.
- Flow Rate Evaluation: Ensure that the flow rate remains consistent with operational demands. Fluctuations can indicate that the adjustments may have introduced instability.
- Leak Detection: Inspect the valve and its connections for leaks. Even minor leaks could negate the effectiveness of the adjustments and lead to inefficiencies.
The benefits of diligent monitoring are substantial. It allows identification of any adverse reactions early, supporting timely intervention before minor issues escalate. Moreover, it ensures that the system runs within the intended operational parameters, avoiding potential disruptions.
Documenting Changes Made
Documenting any changes made during the adjustment process is fundamental for maintenance and future reference. A structured approach to documentation can help maintain clarity and facilitate ongoing management of the system. Important steps in documenting changes include:
- Recording Initial and Adjusted Pressure Levels: Note all relevant pressure values before and after adjustments. This establishes a benchmark for future adjustments.
- Date and Time Stamping: Document when modifications were made. This provides context for changes and assists in troubleshooting should new issues arise.
- Observations: Include observations regarding system performance during post-adjustment monitoring. Noting any irregularities can aid in diagnosing issues down the line.
Maintaining a detailed log not only assists in managing the current state but also serves as a valuable reference for periodic reviews or if further adjustments are needed.
"Documenting changes is as important as making them. Future adjustments rely on past records."
Safety Precautions
Adjusting a pressure reducer valve may seem straightforward, but neglecting safety precautions can lead to serious incidents. Understanding and implementing safety measures is essential for both the individual performing the adjustment and the system involved. These precautions minimize risks associated with pressure systems, which can operate under high pressure and pose various dangers, such as leaks, bursts, or even personal injury. When approaching this task, being vigilant about safety cannot be overstated.
Personal Protective Equipment Recommendations
Wearing the proper personal protective equipment (PPE) during the adjustment process is crucial. Here are some recommended items to ensure safety:
- Safety Glasses: Protects the eyes from potential splashes or flying debris.
- Gloves: Chemical-resistant gloves are advisable since adjustments may expose you to hazardous substances.
- Steel-toed Boots: Protects the feet from heavy objects that might fall or roll over.
- Hearing Protection: If the system generates significant noise, earplugs or earmuffs may be necessary.
In addition to these items, wearing a hard hat can provide added protection in environments where overhead hazards exist. It is imperative that all individuals involved wear these items before commencing work on the valve.
Recognizing Potential Hazards
Understanding potential hazards is a critical component of safety when adjusting a pressure reducer valve. Familiarity with the following risks can prepare you better:
- High Pressure: Systems can be under extreme pressure, which can cause sudden releases if mishandled.
- Chemical Exposure: Fluids within the system may be toxic, flammable, or corrosive. Knowing what is in the system is vital.
- Tripping Hazards: Tools and equipment can create tripping risks in the workspace, leading to accidents.
- Equipment Failure: Failure of the valve or surrounding equipment may lead to dangerous situations. Regular inspection is necessary.
It is important to continuously assess your work environment for these hazards and adapt accordingly. Awareness can significantly mitigate risks while executing the adjustments, allowing for a more controlled and safer procedure.
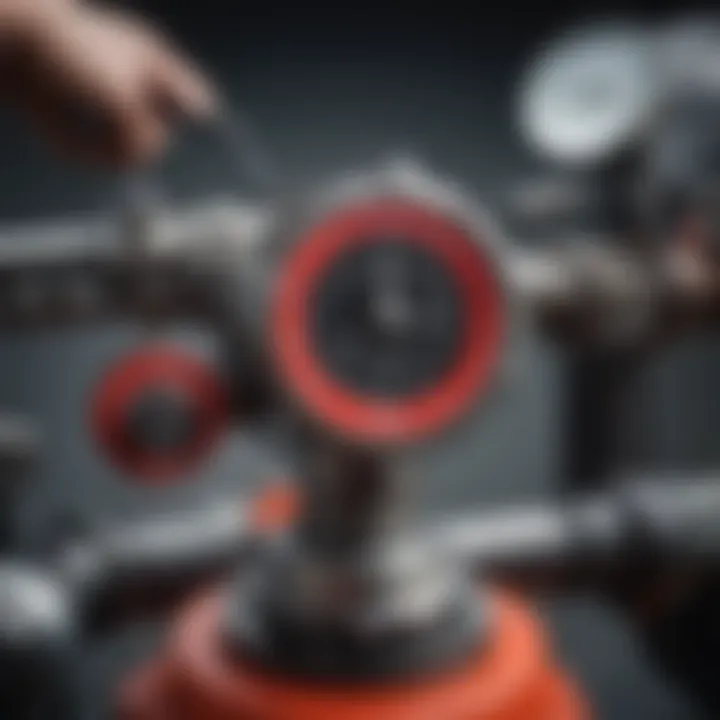


"Safety first. Always take necessary precautions to avoid accidents during valve adjustments."
By adhering to established safety precautions, individuals can ensure a more secure work environment while adjusting pressure reducer valves.
Troubleshooting Issues During Adjustment
Adjusting a pressure reducer valve can sometimes lead to unexpected complications. Therefore, understanding how to troubleshoot these issues is crucial for anyone involved in the adjustment process. Effective troubleshooting can prevent further damage to the system, ensure safety, and maintain the target pressure required for optimal performance.
When adjusting these valves, several common problems may arise. Recognizing these issues early can help avert more significant complications down the line. Effective troubleshooting often leads to quick resolutions and minimizes downtime. It is essential to be aware of the common issues that users may encounter and explore potential solutions accordingly.
In addition, understanding which situations warrant professional assistance can save time and ensure safety. Knowing the limits of one’s expertise is a fundamental aspect of proper maintenance practices.
Common Problems and Solutions
When working with pressure reducer valves, users might encounter a variety of problems. Here are some frequent issues and the potential solutions to address them:
- Inconsistent Pressure Output
- Leakage
- Difficulties in Adjusting the Valve
- Sudden Pressure Spikes
- Noise During Operation
- Solution: Check if there are any clogs in the valve or the associated piping. Clean the valve and inspect for obstructions that may affect performance.
- Solution: Examine all connections to ensure they are securely fastened. If leakage persists, inspecting the seals for wear or damage is vital, as replacing them may resolve the problem.
- Solution: Sometimes, the adjustment mechanism can become stuck due to corrosion or debris. Applying a lubricant may assist in freeing the mechanism, allowing for easier adjustments.
- Solution: This can be indicative of a malfunctioning valve or an issue upstream. Assessing upstream components, such as the pressure gauge or the source, might be necessary to locate the fault.
- Solution: Noises can signal improper installation or the presence of debris in the valve. Conducting routine maintenance checks should help in identifying and resolving the source of the noise.
When to Seek Professional Assistance
While many issues can be addressed by users with basic troubleshooting knowledge, some situations necessitate the involvement of a professional. Knowing when to call for help can prevent accidents and prolong the lifespan of the equipment. Here are scenarios to watch out for:
- Persistent Issues: If problems persist despite trying various solutions, it may be time to consult an expert. This indicates a more complex issue that could require specialized knowledge.
- Safety Concerns: Any time there is a significant risk of injury or damage to property, it is best to reach out to a qualified technician. Pressure systems can be hazardous if not handled correctly.
- Lack of Knowledge: When the user does not feel confident in resolving an issue due to a lack of understanding, seeking professional advice is a wise choice.
- Regulatory Compliance: In some cases, making adjustments to systems may require following specific regulations. A professional can ensure compliance with local laws and standards.
Through careful attention to detail and proactive measures, users can minimize problems associated with adjusting pressure reducer valves. Being equipped with the right knowledge is crucial for maintaining efficiency and safety.
Closure
The conclusion of this article underscores the critical importance of proper adjustment and maintenance of pressure reducer valves. These components are not just mere mechanical parts; they are vital for maintaining optimal pressure levels within various systems. Ensuring these valves function correctly can significantly impact system performance, safety, and efficiency.
Summary of Key Points
To summarize the essential elements discussed throughout the article:
- Understanding the Mechanism: Knowing how pressure reducer valves work lays the foundation for effective adjustments. The mechanisms involved and the different types highlight the importance of selection based on application.
- Pre-Adjustment Checks: Before making any adjustments, it’s crucial to assess current pressure levels and identify specific requirements. This allows tailored action for the desired outcome.
- Step-by-Step Adjustments: A structured approach to adjusting the valve, from gathering necessary tools to making initial adjustments, ensures clarity and minimizes risk. Testing pressure levels post-adjustment verifies effectiveness.
- Safety and Troubleshooting: Awareness of safety precautions and common troubleshooting techniques during adjustment helps prevent accidents and resolves potential issues efficiently.
Encouragement for Proper Maintenance Practices
Lastly, consistent maintenance of pressure reducer valves is essential. Neglecting these components can lead to recurring issues, inefficiencies, or even safety hazards.
Consider implementing a routine maintenance schedule that includes:
- Regular Inspections: Check for leaks, wear, and corrosion. Noticing small issues can prevent larger failures later.
- Documentation: Keep precise records of any adjustments made, alongside pressure readings and performance metrics. This data can be invaluable for future reference.
- Training and Awareness: For teams involved with these systems, proper training on maintenance practices can enhance overall safety and efficiency.
By fostering a culture of proactive maintenance and awareness, individuals and organizations can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of their pressure reducer valves. This approach not only safeguards investments but also ensures operational reliability.



